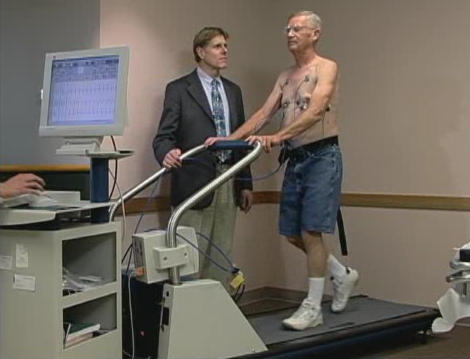
Exercise treadmill test is one of the functional endpoints that CPC’s Endpoint Quality Intervention Program (EQuIP®) has a proven track record of successfully standardizing.
The exercise treadmill test (ETT) is the most rigorous evaluation of maximal walking ability and considered the gold standard test used in therapeutic trials for peripheral artery disease (PAD) and other cardiovascular diseases.
In particular, a graded ETT can effectively study a wide, dynamic range of exercise limitations and provides a consistent and controlled workload environment. Unlike time-limited exercise assessments, the peak walking time from an ETT can represent a true assessment of maximal physiologic performance. ETT is also a good surrogate for an individual’s day-to-day ambulatory function and quality of life.
Despite its advantages, an ETT is only accurate and reproducible if consistently and properly conducted across all sites.